- Java Basic Programs
- Java Programming Examples
- Java Print Hello World
- Java Get Input from User
- Java Print Integer
- Java Add two Numbers
- Java Check Even or Odd
- Java Check Prime or Not
- Java Check Alphabet or Not
- Java Check Vowel or Not
- Check Reverse equal Original
- Java Fahrenheit to Celsius
- Java Celsius to Fahrenheit
- Java Perfect Number Program
- Java Find Quotient Remainder
- Java Days to Seconds
- Java Count Digits in Number
- Java Binary Number Addition
- Java Discount Program
- Java Compute Courier Charge
- Java Find Telephone Bill
- Java Print ASCII Values
- Java Check Palindrome or Not
- Java Check Armstrong or Not
- Generate Armstrong Numbers
- Add two Numbers using Pointers
- Java Mathematical Programs
- Add Subtract Multiply & Divide
- Java Make Calculator
- Java Add Digits of Number
- Java Check Leap Year or Not
- Java Check Divisibility
- Java Find Simple Interest
- Java Find Compound Interest
- Java Print Fibonacci Series
- Java Find nCr nPr
- Calculate Average & Percentage
- Java Calculate Arithmetic Mean
- Java Calculate Student Grade
- Java Print Table of Number
- Java Print Prime Numbers
- Java Add n Numbers
- Java Interchange two Numbers
- Java Reverse Numbers
- Java Swap two Numbers
- Count Positive Negative & Zero
- Find Largest of two Numbers
- Find Largest of three Numbers
- Java Find Factorial of Number
- Java Find HCF & LCM
- Area & Perimeter of Square
- Area & Perimeter of Rectangle
- Area & Circumference of Circle
- Java Conversion Programs
- Java Decimal to Binary
- Java Decimal to Octal
- Java Decimal to Hexadecimal
- Java Binary to Decimal
- Java Binary to Octal
- Java Binary to Hexadecimal
- Java Octal to Decimal
- Java Octal to Binary
- Java Octal to Hexadecimal
- Java Hexadecimal to Decimal
- Java Hexadecimal to Binary
- Java Hexadecimal to Octal
- Java Pattern Programs
- Java Pattern of Stars
- Java Pattern of Alphabets
- Java Pattern of Numbers
- Java Pyramid of Stars
- Java Pyramid of Alphabets
- Java Pyramid of Numbers
- Java Print Diamond Pattern
- Java Print Floyd Triangle
- Java Print Pascal Triangle
- Java Array Programs
- One Dimensional Array Program
- Java Linear Search
- Java Binary Search
- Find Largest Element in Array
- Find Smallest Element in Array
- Java Reverse Array
- Insert Element in Array
- Delete Element from Array
- Java Merge two Array
- Java Bubble Sort
- Java Selection Sort
- Java Insertion Sort
- Java Find Common Elements
- Java Count Even/Odd Number
- Two Dimensional Array Program
- Java Add two Matrices
- Java Subtract two Matrices
- Java Transpose Matrix
- Multiply two Matrices
- Three Dimension Array Program
- Java String Programs
- Java Print String
- Find Length of String
- Java Compare two String
- Java Copy String
- Java Concatenate String
- Java Reverse String
- Delete Vowels from String
- Delete Words from Sentence
- Find Occurrence of a Character
- Java Find Occurrence of a Word
- Occurrence of Each Character
- Java Occurrence of Each Word
- Java Count Repeated Characters
- Java Count Repeated Words
- Java Capitalize Each Word
- Java Count Vowels/Consonants
- Java Extract Numbers
- Java Count Word in String
- Remove Spaces from String
- Java Sort a String
- Java Uppercase to Lowercase
- Java Lowercase to Uppercase
- Java Swap two Strings
- Java Check Anagram or Not
- Java Check Balance Parentheses
- Java Check Password Strength
- Java File Programs
- Java Read File
- Java Write to File
- Read & Display File Content
- Java Copy File
- Java Append Text to File
- Java Merge two File
- List files in Directory
- Java Delete File
- Java Miscellaneous Programs
- Generate Random Numbers
- Java Print Time & Date
- Java Get IP Address
- Java Shutdown Computer
- Java Programming Tutorial
- Java Tutorial
Java Program to Count the Occurrence of Each Character in String
This article is created to cover a program in Java, to count the occurrence of each character in a string entered by user at run-time of the program.
The question is, write a Java program to count and print the occurrence of each characters available in a string. The string must be received by user at run-time. The program given below is its answer:
import java.util.Scanner; public class fresherearth { public static void main(String[] args) { int len, i, k, count, prevLen, arri=0, arrLen=0; String str; char ch; Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter the String: "); str = s.nextLine(); len = str.length(); char[][] arr = new char[len][2]; for(i=0; i<len; i++) { ch = str.charAt(i); count = 0; for(k=0; k<arrLen; k++) { if(ch==arr[k][0]) { prevLen = (arr[k][1]); prevLen = prevLen+1; arr[k][1] = (char)prevLen; count++; break; } } if(count==0) { arr[arri][0] = ch; arr[arri][1] = '1'; arrLen++; arri++; } } for(i=0; i<arrLen; i++) System.out.println(arr[i][0]+ " -> " +arr[i][1]); } }
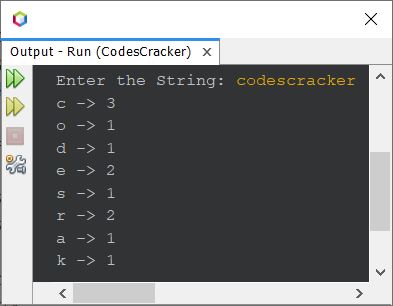
Here is its sample run with user input fresherearth as string to count occurrence of each character available in this given string:
Here is another sample run with user input, Welcome to jobails.com:
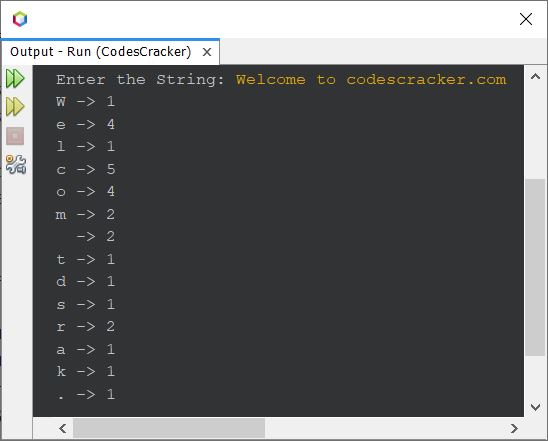
In above sample output, in between the character m and t, the occurrence 2 refers to white space.
In above program, I've created a two dimensional array. That is, array inside array. The inner array is of size 2. Where at the first index, I've placed the character, and at second, I've placed its occurrence. And the whole array of character and its occurrence, is wrapped in an outer array of size equals to the total number of unique characters, available in given string.
Note - Since the array arr is of char data type, therefore before initializing the value of prevLen (an int type variable), we need to typecast the variable into char. So I've done using (char)prevLen.
The dry run of above program with user input fresherearth goes like:
- Initial values, arri=0, arrLen=0, str="fresherearth" (entered by user)
- Using the statement
len = str.length();
the length of entered string, that will be 12, will get initialized to len variable - Now a character array named arr is declared, whose maximum size is 12. That is, the array arr can contain maximum 12 arrays of 2-elements each. It occupies its maximum size, only if all characters entered by user are unique. This array is created to store character and its occurrence.
- As soon as the occurrence increases, of any character, the size will get decreases. Because, we do not need to store that duplicate character, rather we need to increment the previous occurrence value by 1 more, of that character.
- Now the execution of for loop begins
- Initially i=0, and since the condition i<len or 0<12 evaluates to be True. therefore program flow goes inside the loop
- Using the statement
ch = str.charAt(i);
the character at index number i in str, will get initialized to ch - Therefore str.charAt(0) or 'c' will get initialized to ch. And then using the next statement, 0 will get initialized to count variable. This variable is used to check whether the current character is available in the character array arr or not
- Now the execution of inner for loop begins
- Initially k=0 and the condition k<arrLen or 0<0 evaluates to be False. Therefore program flow does not goes inside this loop
- After this loop, the condition of if will gets evaluated. That is, the condition count==0 or 0==0 evaluates to be True. Therefore program flow goes inside the if's block and evaluates all the four statements available inside it
- So, ch or 'c' will get initialized to arr[arri][0] or arr[0][0]. Similarly, arr[0][1]='1', arrLen=1, arri=1 (by incrementing its value)
- Now the value of i will get incremented. That is i=1 and the condition i<len (condition of outer for loop), or 1<12 evaluates to be True again
- Therefore, program flow again goes inside the loop
- The next character, second character 'o' will get initialized to ch. And count=0 again
- The execution of inner loop begins, again
- That is, k=0 and k<arrLen or 0<1 evaluates to be True, therefore program flow goes inside this loop and the condition ch==arr[k][0] or 'o'==arr[0][0] or 'o'=='c' evaluates to be False. Therefore program flow does not goes inside this block
- The value of k gets incremented, now k=1 and the condition k<arrLen or 1<1 evaluates to be False, this time
- Now the condition (of if) count==0 or 0==0 evaluates to be True. This condition only evaluates to be True, if the current character of str will not be available inside the char array named arr
- Now arr[arri][0] = ch, i.e., arr[1][0] = 'o' and arr[1][1] = '1'. Similarly arrLen=2 and arri=2
- Now the value of i again gets incremented by 1. So i=2
- The condition i<len or 2<12 evaluates to be True again, therefore program flow goes inside the loop, third time
- This process continues, until the condition evaluates to be False
- In this way, when the execution finishes, the character array arr holds the array of unique characters with its occurrences. Where the unique characters are placed at first, and its occurrences are placed at second index of each 1D array inside this 2D array.
« Previous Program Next Program »