- Java Basic Programs
- Java Programming Examples
- Java Print Hello World
- Java Get Input from User
- Java Print Integer
- Java Add two Numbers
- Java Check Even or Odd
- Java Check Prime or Not
- Java Check Alphabet or Not
- Java Check Vowel or Not
- Check Reverse equal Original
- Java Fahrenheit to Celsius
- Java Celsius to Fahrenheit
- Java Perfect Number Program
- Java Find Quotient Remainder
- Java Days to Seconds
- Java Count Digits in Number
- Java Binary Number Addition
- Java Discount Program
- Java Compute Courier Charge
- Java Find Telephone Bill
- Java Print ASCII Values
- Java Check Palindrome or Not
- Java Check Armstrong or Not
- Generate Armstrong Numbers
- Add two Numbers using Pointers
- Java Mathematical Programs
- Add Subtract Multiply & Divide
- Java Make Calculator
- Java Add Digits of Number
- Java Check Leap Year or Not
- Java Check Divisibility
- Java Find Simple Interest
- Java Find Compound Interest
- Java Print Fibonacci Series
- Java Find nCr nPr
- Calculate Average & Percentage
- Java Calculate Arithmetic Mean
- Java Calculate Student Grade
- Java Print Table of Number
- Java Print Prime Numbers
- Java Add n Numbers
- Java Interchange two Numbers
- Java Reverse Numbers
- Java Swap two Numbers
- Count Positive Negative & Zero
- Find Largest of two Numbers
- Find Largest of three Numbers
- Java Find Factorial of Number
- Java Find HCF & LCM
- Area & Perimeter of Square
- Area & Perimeter of Rectangle
- Area & Circumference of Circle
- Java Conversion Programs
- Java Decimal to Binary
- Java Decimal to Octal
- Java Decimal to Hexadecimal
- Java Binary to Decimal
- Java Binary to Octal
- Java Binary to Hexadecimal
- Java Octal to Decimal
- Java Octal to Binary
- Java Octal to Hexadecimal
- Java Hexadecimal to Decimal
- Java Hexadecimal to Binary
- Java Hexadecimal to Octal
- Java Pattern Programs
- Java Pattern of Stars
- Java Pattern of Alphabets
- Java Pattern of Numbers
- Java Pyramid of Stars
- Java Pyramid of Alphabets
- Java Pyramid of Numbers
- Java Print Diamond Pattern
- Java Print Floyd Triangle
- Java Print Pascal Triangle
- Java Array Programs
- One Dimensional Array Program
- Java Linear Search
- Java Binary Search
- Find Largest Element in Array
- Find Smallest Element in Array
- Java Reverse Array
- Insert Element in Array
- Delete Element from Array
- Java Merge two Array
- Java Bubble Sort
- Java Selection Sort
- Java Insertion Sort
- Java Find Common Elements
- Java Count Even/Odd Number
- Two Dimensional Array Program
- Java Add two Matrices
- Java Subtract two Matrices
- Java Transpose Matrix
- Multiply two Matrices
- Three Dimension Array Program
- Java String Programs
- Java Print String
- Find Length of String
- Java Compare two String
- Java Copy String
- Java Concatenate String
- Java Reverse String
- Delete Vowels from String
- Delete Words from Sentence
- Find Occurrence of a Character
- Java Find Occurrence of a Word
- Occurrence of Each Character
- Java Occurrence of Each Word
- Java Count Repeated Characters
- Java Count Repeated Words
- Java Capitalize Each Word
- Java Count Vowels/Consonants
- Java Extract Numbers
- Java Count Word in String
- Remove Spaces from String
- Java Sort a String
- Java Uppercase to Lowercase
- Java Lowercase to Uppercase
- Java Swap two Strings
- Java Check Anagram or Not
- Java Check Balance Parentheses
- Java Check Password Strength
- Java File Programs
- Java Read File
- Java Write to File
- Read & Display File Content
- Java Copy File
- Java Append Text to File
- Java Merge two File
- List files in Directory
- Java Delete File
- Java Miscellaneous Programs
- Generate Random Numbers
- Java Print Time & Date
- Java Get IP Address
- Java Shutdown Computer
- Java Programming Tutorial
- Java Tutorial
Java Program to Find Common Elements between Two Arrays
This article covers a program in Java that find and prints common elements between two given arrays.
Find Common Elements between Two Arrays - Basic Version
The question is, write a Java program to find and print common elements available between two arrays. The array must be received by user at run-time of the program. The program given below is the answer to this question:
import java.util.Scanner; public class fresherearth { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arrOne = new int[5]; int[] arrTwo = new int[5]; int i, j; Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter 5 elements for the first array: "); for(i=0; i<5; i++) arrOne[i] = s.nextInt(); System.out.print("\nEnter 5 elements for the second array: "); for(i=0; i<5; i++) arrTwo[i] = s.nextInt(); System.out.println("\nCommon elements are:"); for(i=0; i<5; i++) { for(j=0; j<5; j++) { if(arrOne[i]==arrTwo[j]) System.out.print(arrOne[i]+ " "); } } } }
The snapshot given below shows the sample run of above Java program with user inputs, 1, 3, 6, 11, 12 as five elements of first, and 45, 11, 90, 3, 10 as five elements of second array:
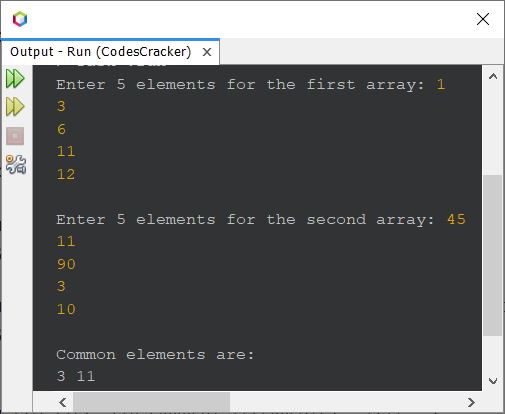
Find Common Elements between Two Arrays - Complete Version
There are some limitations with above program, like what if user wants to enter more elements ?
what there is no common elements available in both arrays ?
what if a single common elements available multiple times in both arrays ?
Also the program given above, does not actually stores the common elements, rather it just prints the element at the time
of comparing.
And if there is no common elements found in both arrays, then the message Common elements are: will get displayed with no elements on output, that will look weird. Therefore let me modify the above program, keeping in mind, to remove all the limitations:
import java.util.Scanner; public class fresherearth { public static void main(String[] args) { int i, j, arrOneSize, arrTwoSize, arrCommonSize, k=0, x, check; Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter the Size of First Array: "); arrOneSize = s.nextInt(); int[] arrOne = new int[arrOneSize]; System.out.print("Enter " +arrOneSize+ " Elements: "); for(i=0; i<arrOneSize; i++) arrOne[i] = s.nextInt(); System.out.print("\nEnter the Size of Second Array: "); arrTwoSize = s.nextInt(); int[] arrTwo = new int[arrTwoSize]; System.out.print("Enter " +arrTwoSize+ " Elements: "); for(i=0; i<arrTwoSize; i++) arrTwo[i] = s.nextInt(); if(arrOneSize<arrTwoSize) arrCommonSize = arrOneSize; else arrCommonSize = arrTwoSize; int[] arrCommon = new int[arrCommonSize]; for(i=0; i<arrOneSize; i++) { for(j=0; j<arrTwoSize; j++) { if(arrOne[i]==arrTwo[j]) { check = 0; for(x=0; x<k; x++) { if(arrCommon[x]==arrOne[i]) { check = 1; break; } } if(check==0) { arrCommon[k] = arrOne[i]; k++; } } } } if(k==0) System.out.println("\nNo common element."); else if(k==1) { System.out.println("\nThere is only one common element."); System.out.println("And the element is: " +arrCommon[0]); } else { System.out.println("\nThere are " +k+ " common elements found."); System.out.print("List of Common Elements: "); for(i=0; i<k; i++) System.out.print(arrCommon[i]+ " "); } } }
Here is its sample run with user inputs, 6 as the size of first array, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 as its six elements. Then 8 as the size of second array, 10, 20, 30, 10, 10, 70, 60, 100 as its eight elements:
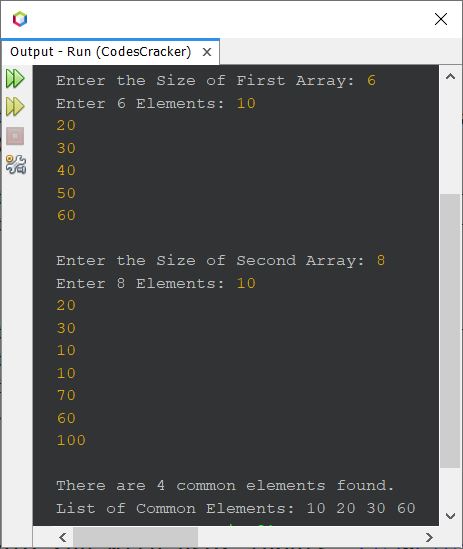
« Previous Program Next Program »