- Digital Electronics Course
- Digital Electronics Tutorial
- Logic Gates
- NAND NOR as a Universal Gate
- Boolean Algebra
- Proof of Theorems and Postulates
- De-Morgan's Theorems
- Duality Principle
- Sum of Products (SOP)
- Product of Sum (POS)
- Canonical SOP Form
- Canonical POS Form
- SOP to Standard SOP
- POS to Standard POS
- Standard SOP to Minimal SOP
- Standard POS to Minimal POS
- Computer Programming
- Learn Python
- Python Keywords
- Python Built-in Functions
- Python Examples
- Learn C++
- C++ Examples
- Learn C
- C Examples
- Learn Java
- Java Examples
- Learn C#
- Learn Objective-C
- Web Development
- Learn HTML
- Learn CSS
- Learn JavaScript
- JavaScript Examples
- Learn SQL
- Learn PHP
Logic Gates and its Types
This article will describe logic gates and their various types. Let's start with its definition.
Definition of Logic Gates
A digital circuit that takes in one or more inputs and produces a single output is called a logic gate. Both the input and the output are digital signals.
Or you can say that a logic gate is an electronic circuit or device that makes the logical decision.
The gate can be constructed from:
- Diodes
- Transistor
- Register
Types of Logic Gates
There are basically seven types of logic gates available that are categorized into three categories:
- Basic Gates
- Universal Gates
- Special Purpose Gates
Let's go over each of the aforementioned logic gate types in detail, including their definitions, boolean equations, and truth tables.
AND Gate
An AND gate is a logic circuit that consists of two or more inputs and only one output.
In an AND gate, the output is high if and only if all the inputs to the gate are high. Otherwise, the output will be low. Here, high indicates 1 and low indicates 0. In a digital circuit, we only talk about 0 and 1.
Symbol of the AND Gate
Here is the symbol for the two-input AND gate:

Here, A and B are the two inputs, and Y is the output.
AND Gate Boolean Equation
Here is the boolean equation of a two-input AND gate:
Y = A.B
AND Gate Truth Table
The table given below represents or shows the truth table of a two-input AND gate:
| Input | Output | |
|---|---|---|
| A | B | Y |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
OR Gate
An OR gate is a logic circuit with two or more inputs and only one output.
The function of an OR gate can be expressed as follows: if either of the two inputs is true, then the output will be true; otherwise, the output will be false. Here, true means 1 and false means 0.
Symbol of the OR Gate
Below is the symbol for the two-input OR gate:
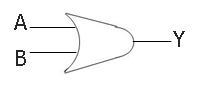
Boolean Expression for OR Gate
The boolean expression of the two-input OR gate will be:
Y = A + B
OR Gate Truth Table
The table given below shows the truth table of an OR gate:
| Input | Output | |
|---|---|---|
| A | B | Y |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
NOT Gate
A NOT gate is used to reverse the input, which means that when the input is true, the output will not be true, implying that the output is false.
Symbol of the NOT Gate
Here is the symbol used for the NOT gate:
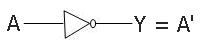
NOT Gate Boolean Expression
The boolean expression of the NOT gate is:
Y = A'
The Truth Table of the NOT Gate
The NOT gate's truth table is as follows:
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
| A | Y |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
NAND Gate
The NAND gate, or NOT-AND gate, is made up of two gates. The first one is an AND gate followed by a NOT gate.
We can use the NAND gate whenever we want to reverse the value of the AND gate's output.
Symbol of the NAND Gate
The symbol of a two-input NAND gate is given below:
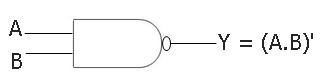
Boolean Expression of the NAND Gate
The boolean expression of a two-input NAND gate will be:
Y = (A.B)'
As we can see from the above expression, it reverses the value of the AND gate output's value.
The NAND Gate Truth Table
The table given below shows the truth table of a two-input NAND gate:
| Input | Output | |
|---|---|---|
| A | B | Y |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
NOR Gate
The NOR gate is a little bit similar to the NAND gate. OR gate is used instead of AND gate in this case.Therefore, we can say that a NOR gate is a combination of an OR gate followed by a NOT gate.
This gate is used to reverse the value of the OR gate's output. It is abbreviated as the NOT-OR gate.
Symbol of the NOR Gate
The symbol used for a two-input NOR gate is:
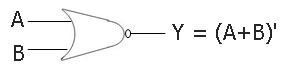
Boolean Expression for NOR Gate
The boolean expression of a two-input NOR gate will be:
Y = (A+B)'
NOR Gate's Truth Table
The table given below shows the truth table of a two-input NOR gate or NOT-OR gate:
| Input | Output | |
|---|---|---|
| A | B | Y |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
XOR Gate
The XOR gate can also be called the EX-OR gate or EOR gate and is pronounced as the Exclusive OR gate.
An exclusive OR gate can have two or more input terminals and only one output terminal.
The XOR Gate's symbol
Here is the symbol given for the two-input XOR gate:
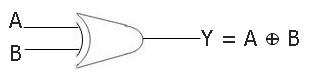
Boolean Expression of the XOR Gate
The boolean expression of a two-input XOR gate is:
Y = A ⊕ B
The XOR Gate Truth Table
The table given below shows the truth table of a two-input XOR gate:
| Input | Output | |
|---|---|---|
| A | B | Y |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
XNOR Gate
XNOR, EX-NOR, or ENOR gates are pronounced as Exclusive NOR or Exclusive NOT-OR gates. Or, to put it another way, exclusive NOR means NOT Exclusive OR. It means it is the reverse of an XOR gate.
This gate is used to reverse the value of the XOR gate.
XNOR Gate Symbol
Below is the symbol of a two-input XNOR gate:
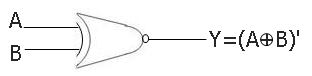
XNOR Gate Boolean Expression
Here is the boolean equation of a two-input XNOR gate:
Y = (A ⊕ B)'
The Truth Table of XNOR Gate
The table given below shows the truth table of a two-input XNOR gate:
| Input | Output | |
|---|---|---|
| A | B | Y |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »