- Python Basic Programs
- Python Program Examples
- Python Print Hello World
- Python Get Input from User
- Python Add Two Numbers
- Add Subtract Multiply Divide
- Python Check Even or Odd
- Python Check Prime or Not
- Python Check Alphabet or Not
- Python Check Vowel or Not
- Python Check Leap Year or Not
- Check Reverse equal Original
- Check Positive Negative Zero
- Python Check Armstrong or Not
- Python Check Palindrome or Not
- Python Check Perfect Number
- Python Find Reverse of Number
- Python Count Digits in Number
- Python Add Digits of Number
- Sum of First and Last Digits
- Python Product of Mid Digits
- Sum of Squares of Digits
- Interchange Digits of Number
- Python Sum of n Numbers
- Python Print ASCII Values
- Python Swap Two Numbers
- Python Swap Two Variables
- Python Fahrenheit to Celsius
- Python Celsius to Fahrenheit
- Python Display Calendar
- Python Days into Years, Weeks
- Find Largest of Two Number
- Find Largest of Three Number
- Python Print Fibonacci Series
- Generate Armstrong Numbers
- Python Make Simple Calculator
- Python Add Binary Numbers
- Binary Number Multiplication
- Python Mathematical Programs
- Find Sum of Natural Numbers
- Find Average of n Numbers
- Python Print Multiplication Table
- Print Table using Recursion
- Python Find Average Percentage
- Python Find Grade of Student
- Find Square Root of Number
- Python Print Prime Numbers
- Find Numbers Divisible by
- Python Find Factors of Number
- Python Find Factorial of a Number
- Python Find HCF & LCM
- Python Kilometres to Miles
- Python Find Area of Square
- Python Find Area of Rectangle
- Python Find Area of Triangle
- Python Find Area of Circle
- Python Find Perimeter of Square
- Find Perimeter of Rectangle
- Python Find Perimeter of Triangle
- Find Circumference of Circle
- Python Simple Interest
- Python Solve Quadratic Equation
- Python Different Set of Operations
- Python Display Powers of 2
- Python Find nCr & nPr
- Python Pattern Programs
- Python Print Pattern Programs
- Python Print Diamond Pattern
- Python Print Floyd's Triangle
- Python Print Pascal's Triangle
- Python List Programs
- Python Count Even/Odd in List
- Python Positive/Negative in List
- Python Even Numbers in List
- Python Odd Numbers in List
- Python Sum of Elements in List
- Sum of Odd/Even Numbers
- Python Element at Even Position
- Python Element at Odd Position
- Python Search Element in List
- Python Largest Number in List
- Python Smallest Number in List
- Python Second Largest in List
- Python Second Smallest in List
- Python Insert Element in List
- Python Delete Element from List
- Python Multiply Numbers in List
- Swap Two Elements in List
- Python 1D Array Program
- Python Linear Search
- Python Binary Search
- Python Insertion Sort
- Python Bubble Sort
- Python Selection Sort
- Remove Duplicates from List
- Python Reverse a List
- Python Merge Two List
- Python Copy a List
- Python Conversion Programs
- Python Decimal to Binary
- Python Decimal to Octal
- Python Decimal to Hexadecimal
- Python Binary to Decimal
- Python Binary to Octal
- Python Binary to Hexadecimal
- Python Octal to Decimal
- Python Octal to Binary
- Python Octal to Hexadecimal
- Python Hexadecimal to Decimal
- Python Hexadecimal to Binary
- Python Hexadecimal to Octal
- Python Matrix Programs
- Python Add Two Matrices
- Python Subtract Two Matrices
- Python Transpose Matrix
- Python Multiply Matrices
- Python String Programs
- Python Print String
- Python Find Length of String
- Python Compare Two Strings
- Python Copy String
- Python Concatenate String
- Python Reverse a String
- Python Swap Two Strings
- Python Uppercase to Lowercase
- Python Lowercase to Uppercase
- Python Check Substring in String
- Python Count Character in String
- Count Repeated Characters
- Python Count Word in Sentence
- Python Count Each Vowels
- Python Capitalize Character
- Python Capitalize Word in String
- Python Smallest/Largest Word
- Remove Spaces from String
- Remove Duplicate Character
- Remove Vowels from String
- Remove Punctuation from String
- Python Remove Word in String
- Python Remove Duplicate Words
- WhiteSpace to Hyphens
- Replace Vowels with Character
- Replace Character in String
- Python Sort String in Alphabetical
- Sort Word in Alphabetical Order
- Extract Number from String
- Python Check Anagram Strings
- Python File Programs
- Python Read a File
- Python Write to File
- Python Append Text to File
- Python Copy Files
- Python Merge Two Files
- Python Counts Characters in File
- Python Count Words in File
- Python File Content in Reverse
- Python Lines Contains String
- Python Delete Line from File
- Python Capitalize Word in File
- Python Replace Text in File
- Replace Specific Line in File
- Python Find Size of File
- Python List Files in Directory
- Python Delete Files
- Python Misc Programs
- Python Reverse a Tuple
- Python Merge Two Dictionary
- Python bytes to String
- Python bytearray to String
- Generate Random Numbers
- Python Print Address of Variable
- Python Print Date and Time
- Python Get IP Address
- Python Shutdown/Restart PC
- Python Tutorial
- Python Tutorial
Python Programming Examples
This article is created to provide you with as many programs as possible in Python, from very basic to advanced. That is, you'll practice with many varieties of programs created in the Python language.
Theory is important, but practice is more important. Understanding how to ride a bike before actually doing so is important. But practicing to ride (actually riding) is more important to becoming an artist in the field of riding.
Therefore, just like this, the theory of Python is important, but actually writing Python programs is more important. Therefore, I've created a lot of programs with different varieties so that you can learn, practice, and feel much better than ever before.
About Python Programming Examples
Since I've created more than 1000 Python programs and all programs can't be covered in a single article, I've divided all these programs into many articles. Each article contains more than one Python program.
Note: All programs written here are well-tested and executed using Python's famous IDE, PyCharm.
Note: Each and every program is provided with its sample output using snapshots. Snapshots are taken while testing the program. Also, all programs are well explained.
Important: If you're new to Python, don't worry; just continue practicing the Python programs given in the next article or page. Since each program is well explained, you'll get to know everything about the topic one by one. And at the end, through this series of Python programs, you'll get to feel much better than ever before.
List of Popular Python Programs
Since I've created more than 1000 Python programs in this section of Python programming examples, they've been divided into many articles. But here is a list of some popular ones:
- Print Hello World
- Get Input from User
- Add Two Numbers
- Check Leap Year or Not
- Add Digits of Number
- Check Armstrong Number or Not
- Find Sum of n Numbers entered by User
- Add Two Binary Numbers
- Decimal to Binary Conversion
- Binary to Hexadecimal Conversion
- Print Pattern of Stars, Pyramids, and Numbers
- Add Two Matrices
- Concatenate Two Strings
- Remove a Word from a String
- Lowercase to Uppercase Conversion
- Append Text to File
- Capitalize Each Word in File
- Print Date and Time
- Shutdown and Restart Computer
Python Demo Programs
The series of Python programming examples has begun with the following article. But for now, let's see some programs written in Python over here to get more interest in Python.
Important: If you feel uncomfortable while reading the code given below, don't worry about it; continue the series from the next article. You'll learn everything there is to know about Python one by one.
Python Example No.1
This is the simplest Python program that uses print() to print the value passed as its argument or inside its braces.
print("Welcome to the World of Python!")
If you run the above program, here is the output you'll see:
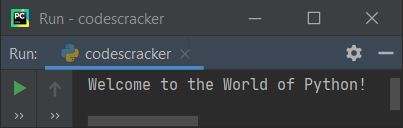
In the above program, there are two lines of code; the first line is a comment. Python treats anything that begins with the # (hash) symbol as a comment. The compiler ignores or doesn't execute anything written after #.
And the second line uses print() to output the thing written inside its braces. For example, consider the following Python program:
# print("Welcome to the World of Python!") text = "Welcome to the World of Python!" print(text)
produces the same output as the previous program. The first line in the preceding program is commented with #. That is, I've added # before the first line's code, so that the compiler ignores it and this line of code doesn't get executed.
Now the last two lines are used to output the same thing as the previous program but in a different way. That is, instead of directly printing the string (anything inside a single (') or double ('') quote is treated as a string), I've used a variable named text. The string gets initialized in this variable, and I've printed the value of this variable using print().
Note: While putting the variable text inside the braces of print(), I've not used double quotes (""). Because if I include a double quote, then the text variable gets treated as a string instead of a variable. And the output you will get should be text, not "Welcome to the World of Python!"
Python Example Program No.2
This is the second demo program in the Python programming examples series.
print("Enter Your Name: ") name = input() print("\nHello", name, "\nWelcome to jobails.com")
Now if you execute or run this program, here is the initial output you'll see:
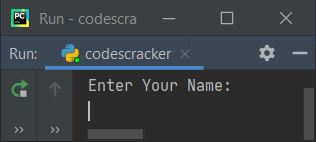
Now supply the input, that is, write your name, say Robert, and press the ENTER key. Here is the output you'll see:
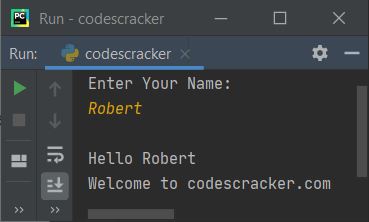
Using print() in the preceding program, a message reading "Enter Your Name" is printed on the output.And using input(), I've received the name of the user as input, and whatever name the user enters gets initialized to the name variable.
And using print() again, I've printed the value of name along with some extra things. The n is used to insert a newline. Therefore, the following statement is true:
print("\nHello", name, "\nWelcome to jobails.com")
states that:
- a newline
- The string "Hello" is then used.
- the value of name
- once more a newline
- yet another string "Welcome to jobails.com"
gets printed on the output. That is, if the user enters the name ABC, the output will look like this:
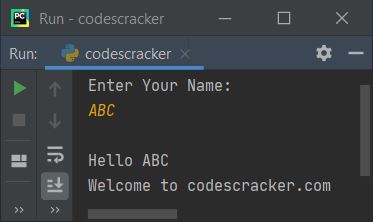
Python Program No.3
This program is created using the if-else statement of Python. Let's have a look:
print("Guess a Number: ") num = input() num = int(num) if num>10 and num<20: print("\nCorrect Guess!") else: print("\nIncorrect Guess!")
Here is its initial output:
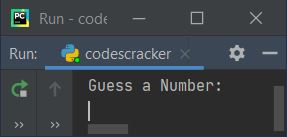
Now guess a number and type it, say 13, and press the ENTER key to see the output as shown in the snapshot given below:
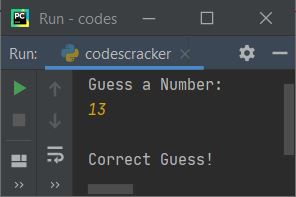
Since I've guessed and typed a number that is greater than 10 and less than 20, therefore, I've seen the output as shown in the above snapshot.
By default, when using the input() function to receive input, the received value is treated as a string-type value. Therefore, using the int() method, I've converted the entered value to its integer equivalent.
And using the if statement, I've applied a condition, which is num>10. The compiler checks whether the value of num is greater than 10 or not. Because its value (13) is greater than 10, this condition evaluates to true. Now that I've used the "and" keyword, the second condition also evaluates to true, allowing the statement contained within its body to be executed. Because the second condition also evaluates to be true, program flow goes inside if's body and executes the statement that prints Correct Guess! as output.
And if either of the two conditions is false, the program flow executes else's body, as shown in the following sample run of the above program with user input 34:
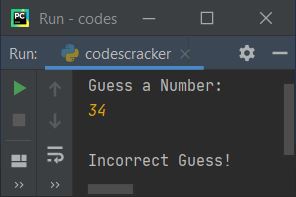
Python Program No.4
This is program number four, and it checks whether the user is a robot or not in the most basic way possible.
print("Are you a Robot ? ") chk = input() if chk == "yes": print("\nSorry!\nRobots aren't Allowed here!") else: print("\nWelcome to jobails.com!")
Here is its sample run with user input, "yes":
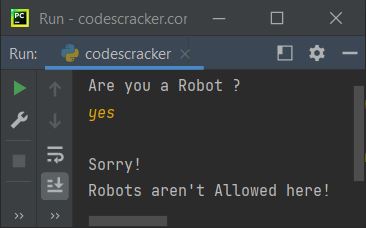
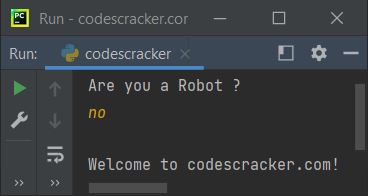
Here's another example with user input, "no".
And this is the third sample run with user input 123.
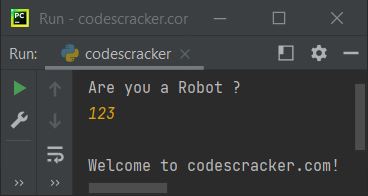
The above program is written in such a way that the input is first received via input() and then initialized to chk. Now, using if again, I've compared the value of chk with "yes." That is, if its value is "yes," then the condition evaluates to be true, and program flow goes inside its body and executes the statement that prints a message saying, "Robots are not allowed!"
But if the user enters anything that is not equal to "yes," that means that the condition evaluates to be false, so the counterpart of the if statement, that is, else's statement(s), gets executed.
Python Program No.5
This is the last demo program of this Python exercise (examples) series.
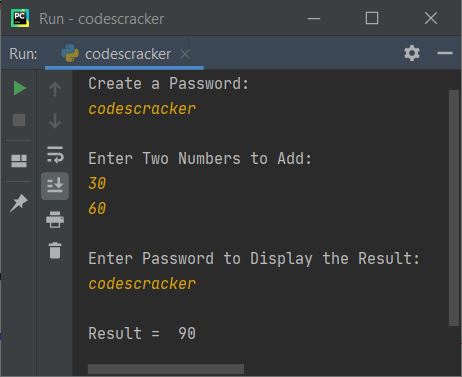
print("Create a Password: ") cp = input() print("\nEnter Two Numbers to Add: ") numOne = int(input()) numTwo = int(input()) print("\nEnter Password to Display the Result: ") ep = input() if cp == ep: sum = numOne + numTwo print("\nResult = ", sum) else: print("\nWrong Password!")
Here is the initial output produced after running the above program:
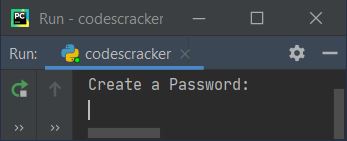
Now create a password, say "fresherearth," and press the ENTER key. Here is the output you'll see
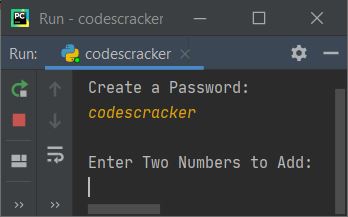
Now enter any two numbers, say 30 and 60, one by one. Here is the output after supplying these two numbers:
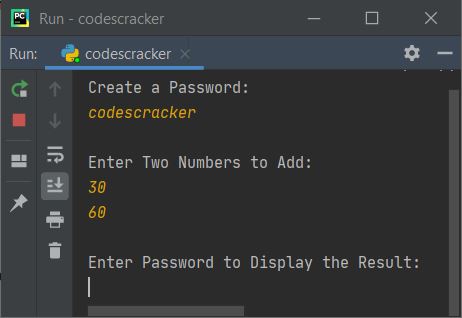
Until you enter the correct password, the result will not be displayed.Here is the output after entering the correct password, which is fresherearth:
Last message before starting the series of Python examples
To learn Python practically, you must complete all of the Python programs in this series, beginning on the following page. Practice these Python programs to feel comfortable in the Python world.
Many Python programs are available, ranging from How to Print Hello World to Shutdown and Restart Computer Using Python Code.
Other Language Programming Examples
« Python Tutorial Next Program »