- Java Programming Basics
- Java Tutorial
- Java Overview
- Java Environment Setup
- Java Program Structure
- Java Basic Syntax
- Java First Program
- Java Constants
- Java Separators
- Java Keywords
- Java Data Types
- Java Data Types
- Java Integers
- Java Floating Point
- Java Characters
- Java Booleans
- Java Numbers
- Java Programming Variables
- Java Variables
- Java Variable Types
- Java Variable Scope
- Java Type Conversion
- Java Type Casting
- Java Auto Type Promotion
- Java Type Promotion Rules
- Java Programming Arrays
- Java Arrays
- Java One Dimensional Array
- Java Multidimensional Array
- Java Programming Operators
- Java Operators
- Java Arithmetic Operators
- Java Increment Decrement
- Java Bitwise Operators
- Java Left Shift
- Java Right Shift
- Java Relational Operators
- Java Boolean Logical Operators
- Java Ternary(?) Operator
- Java Operator Precedence
- Java Control Statements
- Java Decision Making
- Java if if-else if-else-if
- Java switch Statement
- Java Loops
- Java while Loop
- Java do-while Loop
- Java for Loop
- Java for-each Loop
- Java Nested Loops
- Java break Statement
- Java continue Statement
- Java Class Object Method
- Java Classes and Objects
- Java Class
- Java Object
- Java new Operator
- Java Methods
- Java Constructors
- Java this Keyword
- Java Stack
- Java Overloading Recursion
- Java Method Overloading
- Java Constructor Overloading
- Java Object as Parameter
- Java Call by Value Reference
- Java Returning Objects
- Java Recursion
- Java Modifier Types
- Java Encapsulate Poly String
- Java Encapsulation
- Java Polymorphism
- Java Nested Inner Class
- Java Strings
- Java Command Line Arguments
- Java Variable Length Arguments
- Java Inheritance Abstraction
- Java Inheritance
- Java super Superclass
- Java Multilevel Hierarchy
- Java Method Overriding
- Java Abstraction
- Java Packages Interfaces
- Java Packages
- Java Access Protection
- Java Import Statement
- Java Interfaces
- Java Programming Exceptions
- Java Exception Handling
- Java try catch
- Java throw throws
- Java finally Block
- Java Built In Exceptions
- Java Exception Subclasses
- Java Chained Exceptions
- Java Multithreading
- Java Multithreading
- Java Thread Model
- Java Main Thread
- Java Create Thread
- Java Thread Priorities
- Java Synchronization
- Java Inter Thread Communication
- Java Suspend Resume Stop Thread
- Java Get Thread State
- Java Enum Autobox Annotation
- Java Enumerations
- Java Type Wrappers
- Java Autoboxing
- Java Annotation
- Java Marker Annotations
- Java Single Member Annotation
- Java Built In Annotations
- Java Type Annotations
- Java Repeating Annotations
- Java Data File Handling
- Java Files I/O
- Java Streams
- Java Read Console Input
- Java Write Console Output
- Java PrintWriter Class
- Java Read Write Files
- Java Automatically Close File
- Java Programming Advance
- Java Date and Time
- Java Regular Expressions
- Java Collections Framework
- Java Generics
- Java Data Structures
- Java Network Programming
- Java Serialization
- Java Send Email
- Java Applet Basics
- Java Documentation
- Java Programming Examples
- Java Programming Examples
Java Separators
In Java, there are a few characters that are used as separators. The most commonly used separator in Java is the semicolon (;). As you have seen, it is used to terminate the statements.
The separators are listed in the following table :
| Symbol | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ( ) | Parentheses | Used to contain the lists of parameters in method definition and invocation. Also used for defining the precedence in expressions, containing expressions in control statements, and surrounding cast types. |
| { } | Braces | Used to contains the values of automatically initialized arrays. Also used to define a block of code, for classes, methods, and local scopes. |
| [ ] | Brackets | Used to declare array types. Also used when dereferencing array values. |
| ; | Semicolon | Terminates the statements |
| , | Comma | Separates consecutive identifiers in a variable declarations. Also used to chain statements together inside a for statement |
| . | Period | Used to separate packages names from subpackages and classes. Also used to separate a variable or method from a reference variable. |
| :: | Colons | Used to create a method or constructor reference (Added by JDK 8) |
Separators Example
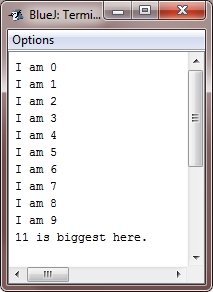
Following Java program contains some separators :
/* Java Program Example - Java Separators
* This program contains some Separators
*/
class JavaProgram
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i, j=10, k=11; // uses comma or , separator
for(i=0; i<j; i++) // uses parentheses or () separator
{ // uses braces or {} separator
System.out.println("I am " + i);
}
System.out.println(k + " is biggest here.");
}
}
The sample run of the above Java program is shown here :
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »