- Java Programming Basics
- Java Tutorial
- Java Overview
- Java Environment Setup
- Java Program Structure
- Java Basic Syntax
- Java First Program
- Java Constants
- Java Separators
- Java Keywords
- Java Data Types
- Java Data Types
- Java Integers
- Java Floating Point
- Java Characters
- Java Booleans
- Java Numbers
- Java Programming Variables
- Java Variables
- Java Variable Types
- Java Variable Scope
- Java Type Conversion
- Java Type Casting
- Java Auto Type Promotion
- Java Type Promotion Rules
- Java Programming Arrays
- Java Arrays
- Java One Dimensional Array
- Java Multidimensional Array
- Java Programming Operators
- Java Operators
- Java Arithmetic Operators
- Java Increment Decrement
- Java Bitwise Operators
- Java Left Shift
- Java Right Shift
- Java Relational Operators
- Java Boolean Logical Operators
- Java Ternary(?) Operator
- Java Operator Precedence
- Java Control Statements
- Java Decision Making
- Java if if-else if-else-if
- Java switch Statement
- Java Loops
- Java while Loop
- Java do-while Loop
- Java for Loop
- Java for-each Loop
- Java Nested Loops
- Java break Statement
- Java continue Statement
- Java Class Object Method
- Java Classes and Objects
- Java Class
- Java Object
- Java new Operator
- Java Methods
- Java Constructors
- Java this Keyword
- Java Stack
- Java Overloading Recursion
- Java Method Overloading
- Java Constructor Overloading
- Java Object as Parameter
- Java Call by Value Reference
- Java Returning Objects
- Java Recursion
- Java Modifier Types
- Java Encapsulate Poly String
- Java Encapsulation
- Java Polymorphism
- Java Nested Inner Class
- Java Strings
- Java Command Line Arguments
- Java Variable Length Arguments
- Java Inheritance Abstraction
- Java Inheritance
- Java super Superclass
- Java Multilevel Hierarchy
- Java Method Overriding
- Java Abstraction
- Java Packages Interfaces
- Java Packages
- Java Access Protection
- Java Import Statement
- Java Interfaces
- Java Programming Exceptions
- Java Exception Handling
- Java try catch
- Java throw throws
- Java finally Block
- Java Built In Exceptions
- Java Exception Subclasses
- Java Chained Exceptions
- Java Multithreading
- Java Multithreading
- Java Thread Model
- Java Main Thread
- Java Create Thread
- Java Thread Priorities
- Java Synchronization
- Java Inter Thread Communication
- Java Suspend Resume Stop Thread
- Java Get Thread State
- Java Enum Autobox Annotation
- Java Enumerations
- Java Type Wrappers
- Java Autoboxing
- Java Annotation
- Java Marker Annotations
- Java Single Member Annotation
- Java Built In Annotations
- Java Type Annotations
- Java Repeating Annotations
- Java Data File Handling
- Java Files I/O
- Java Streams
- Java Read Console Input
- Java Write Console Output
- Java PrintWriter Class
- Java Read Write Files
- Java Automatically Close File
- Java Programming Advance
- Java Date and Time
- Java Regular Expressions
- Java Collections Framework
- Java Generics
- Java Data Structures
- Java Network Programming
- Java Serialization
- Java Send Email
- Java Applet Basics
- Java Documentation
- Java Programming Examples
- Java Programming Examples
Java Write to Console Output
Console output is most easily accomplished with print() and println() methods, as described earlier. These methods are defined by the class PrintStream which is the type of object referenced by System.in. Even though System.out is a byte stream, using it for a simple program output is still acceptable.
Because the PrintStream is an output stream derived from the OutputStream, it also implements the low-level method write(). Thus, write() can be used to write to the console. The simplest form of write() defined by the PrintStream is shown below :
void write(int byteval)
This method writes the byte specified by byteval. Although byteval is declared as an integer, only the low-order eight bits are written. Following is a short example that uses write() to output the character 'X' followed by a newline to the screen:
/* Java Program Example - Java Write Console Output
* This program writes the character X followed by newline
* This program demonstrates System.out.write() */
class WriteConsoleOutput
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int y;
y = 'X';
System.out.write(y);
System.out.write('\n');
}
}
This Java program will produce the following output:
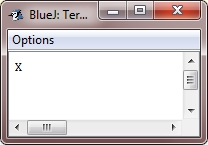
You will not often use write() to perform console output (although doing so might be useful in some situations) because print() and println() are substantially easier to use.
Examples on Files in Java
Here are some examples related to files in Java, you can go for.
- Read File in Java
- Write to File Java
- Read & Display File in Java
- Copy File in Java
- Merge two Files in Java
- List files in a Directory Java
- Delete File in Java
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »